Fatigue Crack Growth Models
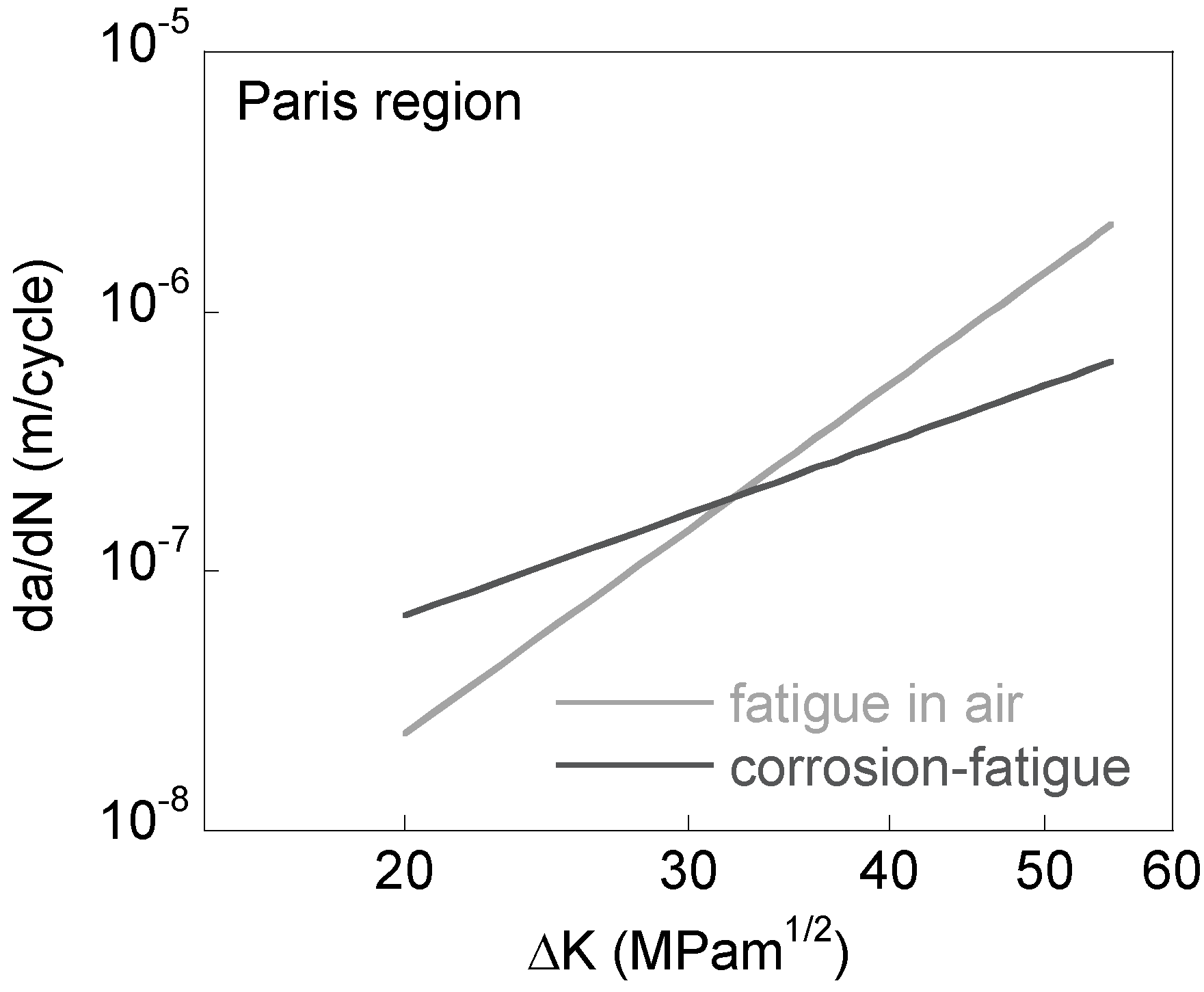
Experimental data and analytical models have shown that a growing fatigue crack produces a plastic wake. This, in turn, leads to residual compressive stresses acting over the crack faces during the unloading portion of the fatigue cycle. This crack closure effect results in an applied stress intensity factor during unloading which is greater than that associated with the Kmin, thus producing a crack-driving force which is less than ΔK = Kmax − Kmin. Life predictions which do not account for this crack closure effect give inaccurate life estimates, especially for fully reversed loadings. This paper discusses the development of a crack closure expression for the 4- point bend specimen using numerical results obtained from a modified strip-yield model. Data from tests of eight 4-point bend specimens were used to estimate the specimen constraint factor (stress triaxiality effect). The constraint factor was then used in the estimation of the crack opening stresses for each of the bend tests. The numerically estimated crack opening stresses were used to develop an effective stress intensity factor range, ΔKeff The resulting crack growth rate data when plotted versus ΔKeffPirate free games download. resulted in a material fatigue crack growth rate property curve independent of test specimen type, stress level, and R-ratio. Fatigue crack growth rate data from center-cracked panels using Newman's crack closure model, from compact specimens using Eason 's R-ratio expression, and from bend specimens using the model discussed in this paper are all shown to fall along the same straight line (on log-log paper) when plotted versus ΔKeff, even though crack closure differs for each specimen type.

Fatigue Crack Growth Models List
Fracture Mechanics and Fatigue Crack Growth Analysis software tool. Influences of Retardation Models on Crack Growth Predictions; 3. FATIGUE CRACK GROWTH, FCG (OVERVIEW).The presence of a crack can significantly reduce the life of a component or structure.To make life estimations for fatigue crack growth and damage tolerant design, the following information are often needed: –The stress intensity factor, K. Apache tomcat version 7 download. –The fracture. Fatigue crack growth governed by the Paris law 12 For linear elastic materials, Griffith’sapproach says that a crack extends if the thermodynamic crack driving force, characterized by the energy release rate G (Fig. 6), becomes equal or larger than the crack growth resistance, R (Griffith, 1921), whereas the Irwin (1957) approach postulates.
Fatigue Crack Growth Models 2016
Recent advances in fatigue crack growth modeling. A model for crack closure with two microscopic crystallographic slip directions is used to model microscopic cracks. The model predicts variations in closure levels as the orientations of the two slip directions, with respect to. 13 (20) Crack closure (R) Elber, in 1970, discovered that crack closure exists in cyclic loading, even for loads that are greater than zero. This crack closure will decrease the fatigue crack growth rate by reducing the effective stress intensity range The stress intensity rate.